What are Resolution, Accuracy & Repeatability
Understanding resolution, accuracy and repeatability is critical to specifying a position sensor. This paper defines these terms and discusses how they relate to overall system performance.
How to Choose the Right Sensor in Ambient Conditions
One of the key considerations while choosing the perfect set of sensors for your robotic designs include their resistance to ambient situations such as temperature, lights, interferences and obstructions.
High Performance Inertial Sensors for Robotic Systems
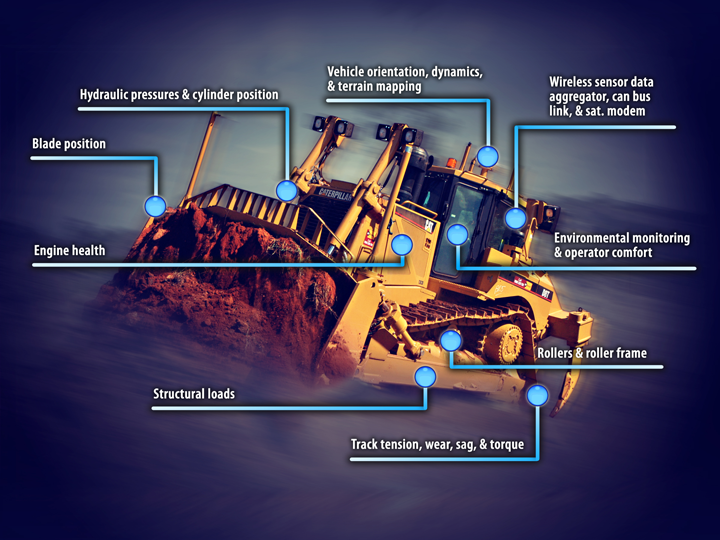
The next generation of robotic systems require high performance inertial sensors but also demand high volume, low cost solutions.
How to Improve Worker Safety Around Robotics
Industrial robots offer increasingly compelling opportunities to help companies get more done and promote consistency in the workplace. Robot safety is another area of concern, especially since robots can reduce some of the risks that cause accidents.
Choosing the Right Inertial Sensor for your Robot
The latest generation inclinometers provide much more stable performance and higher accuracy.
Robot Sensor Market Outlook
The Robot Sensors Market has developed rapidly and boasts of an extensive product base, with estimated earnings of over USD 2 billion in 2017.
The use of Inertial Sensors in Robotics
The primary uses for inertial sensors are platform stability and global positioning, but we are seeing increasing use as feedback in articulated limbs.
7 Reasons Your Life Depends on an Accurate IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) in a Self-Driving Car
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is a device that directly measures the three linear acceleration components and the three rotational rate components (6-DOF) of a vehicle.
How Industrial Self-driving Vehicles Use Sensors for Localization and Mapping
OTTO self-driving vehicles depend on three different sensors to identify its current position as well as to navigate where and how it needs to travel from point A to point B. As in any dense and dynamic environment, elements in OTTOs path can change minute to minute
Industrial Robots: Encoders for Tool Center Point Accuracy
The use of secondary encoders on all of a robots axes, as well as the use of linear encoders for positioning the robot relative to the workpiece, enables a level of accuracy at the tool center point
Interview with Shaoshan Liu and Zhe Zhang of PerceptIn
Using our technology, we are able to reduce the cost of the whole vehicle (including the chassis, the computing hardware, and the sensing hardware, and the software stack) under $10,000 USD.
Q&A with Hillcrest Labs - High Value AHRS/IMUs Enable Low Cost Robot Navigation
The module allows rapid development of new robots by providing all the sensors and sensor processing software in one compact, pre-calibrated device with multiple interfaces supported to meet varying developer requirements.
Soft Stretchy Sensors
When the sensor is integrated into a wearable device and placed across a joint, it is stretched when the joint moves. We can correlate the joint's movement and sensor's capacitance change in order to monitor motion.
Sensors Expo & Conference Partners with Xconomy for Robo Madness West co-location
5th annual event to feature brightest minds and hottest technologies in the world of robotics
New Open Loop Current Transducers With Near Closed Loop Performance
Measured performance is at the level expected and increases the range of applications which may be addressed by open loop transducers instead of more complex solutions.
Records 1 to 15 of 39
Featured Product

REIKU's Cable Saver™ - The Most Versatile Modular Robotic Cable Management Solution
REIKU's Cable Saver™ Solution eliminates downtime, loss of revenue, expensive cable and hose replacement costs, maintenance labor costs. It's available in three sizes 36, 52 and 70 mm.
All of the robots cables and hoses are protected when routed through the Cable Saver™ corrugated tubing.The Cable Saver™ uses a spring retraction system housed inside the Energy Tube™ to keep this service loop out of harms way in safe location at the rear of the Robot when not required. The Cable Saver™ is a COMPLETE solution for any make or model of robot. It installs quickly-on either side of the robot and has been tested to resist over 15 million repetitive cycles.
REIKU is committed to providing the most modular, effective options for ensuring your robotic components operate without downtime due to cable management.
www.CableSaver.com









.jpg)



