Adoption of Digital Twins Set to Accelerate with the Latest Release of Duality's Falcon Platform Powered by Unreal Engine
Digital twin simulation is emerging as a powerful resource for solving complex problems in AI, robotics, and smart system development. It can bring understanding of the physical world to AI models
How Simulation Can Secure Your Robotics Investment
Robotics simulation can be defined as a digital tool used to engineer robotics-based automated production systems. Essentially, robot simulation employs a digital representation to enable dynamic interaction with robot models and machines in a virtual environment.
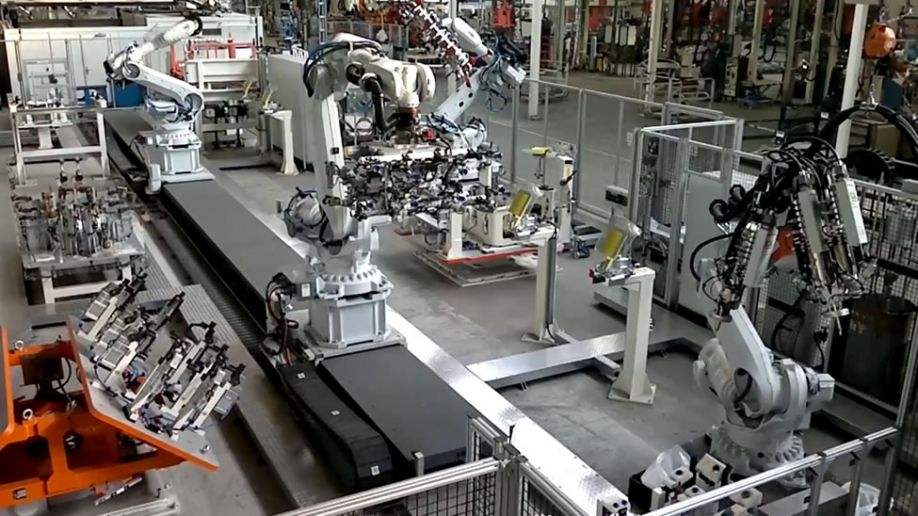
Bringing Advanced Automation To Automotive Industry
In a recent project for Mercedes-Benz (Daimler AG) RobCo S.W.A.T. used RoboDK software to simulate ABB and Motoman robots working on a range of automotive manufacturing tasks including assembly and painting.
Benefits of Developing a Palletizing Simulation
Building a simulation for a palletizing cell helps the integrator and customer start on the same page. Once rate, product, and pallet information is input into the software, realistic cycle times can be shown for any layout/configuration.
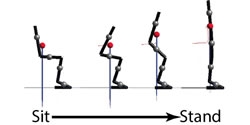
Utilizing MapleSim to Improve Assisted Living Devices
We took biomechanical data from actual human trials and applied them to a robotic model that mimics human movements when transitioning between sitting and standing positions.
How Using the Latest 3D Simulation Software for Vision Guided Robotic Applications Will Save You Time and Money
It is easy to imagine the time saved by using the latest simulation tools to develop vision guided robotic applications.
Altair and Maplesoft Partner to Embed MapleSim Modelica Engine within Model-based System Development Technology
Altair joins the rapidly growing Modelica community for multi-domain simulation
How Sensorimotor Intelligence May Develop
From Institute of Science and Technology Austria:
Robotic systems controlled by a neural network spontaneously develop self-organized behaviors. Researchers propose a novel learning rule in PNAS to explain the development of sensorimotor intelligence.
It is fascinating to observe a robot exploring its physical possibilities and surroundings, and subsequently developing different self-taught behaviors without any instructions. In their paper (DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1508400112) published on October, 26, 2015 in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences), Professor Ralf Der from the Max Planck Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences, und Georg Martius, Postdoc and Fellow at the Institute for Science and Technology (IST Austria), demonstrate the emergence of sensorimotor intelligence in robots based on their proposed learning rule...
... To test their hypothesis, the authors use bioinspired robots consisting of a humanoid and a hexapod robot in physically realistic computer simulations. The robots receive sensory input from their bodies but are not given any form of instruction or task. What can then be observed is a rich spectrum of rhythmic behaviors of the robots as they explore various movements. Solely because of the tight coupling of environment, body, and brain (in this case an artificial neural network), the robots can obtain feedback from their situation and adapt quickly. This, together with a simple, learned self-model, allows them to develop a form of sensorimotor intelligence... ( full article ) ( paper ) ( videos and other materials )
Simulating Clearpath Robots In Maplesim
If your robotics research depends on accurate models, you may want to consider looking at MapleSim® 2015 - a high performance physical modeling and simulation tool developed by Maplesoft™.
Records 1 to 9 of 9
Featured Product

DESTACO - Revolutionizing Industrial Automation
Looking for a reliable solution to enhance your automation process? Look no further than the DESTACO Robohand Grippers. These grippers are designed for the modern world of robotics, offering unparalleled performance and precision. Whether you need to grip fragile items, irregularly shaped objects, or heavy-duty components, the DESTACO Robohand Grippers have got you covered. Their modular design allows for quick and easy customization, ensuring a perfect fit for your application.