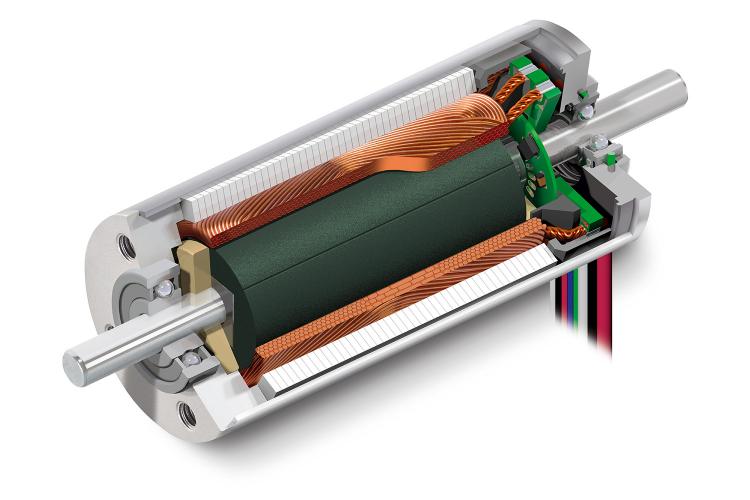
Understanding Torque and Speed in Electric Motors
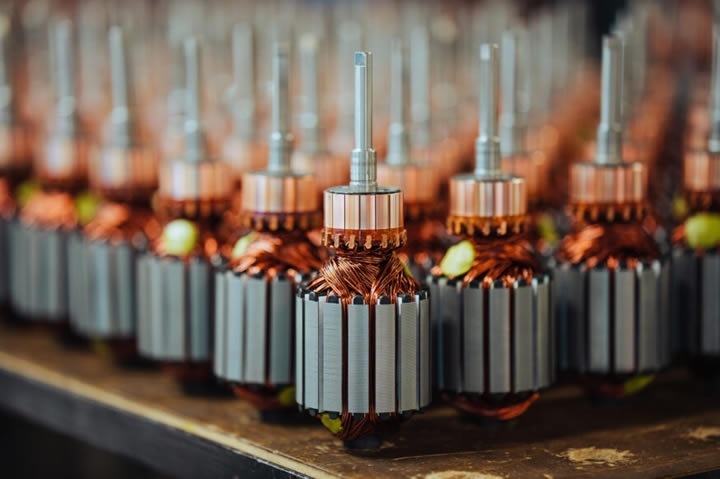
The higher the torque, the greater the ability to rotate heavy objects, overcome tough resistance or to transport objects vertically. Applications which rely on high torque can include hoists and cranes, as well as industrial mixing machines.
Walking naturally with artificial foot
The gait becomes more harmonious, more stable and less tiring. An intelligent controller finds the correct gait rhythm and a brushless motor from FAULHABER provides the necessary propulsion.
Testing drive systems virtually - Simulink library for development and digital twin.
How will the drive actually behave in the real-life application? For brushless DC-motors from FAULHABER, this question can be answered without any hardware whatsoever.
Robots speeding up material handling
With omnidirectional movement and smart docking with virtually any warehouse cart in under 20 seconds, these new robots are making material handling faster and safer.
At least 60 million strokes
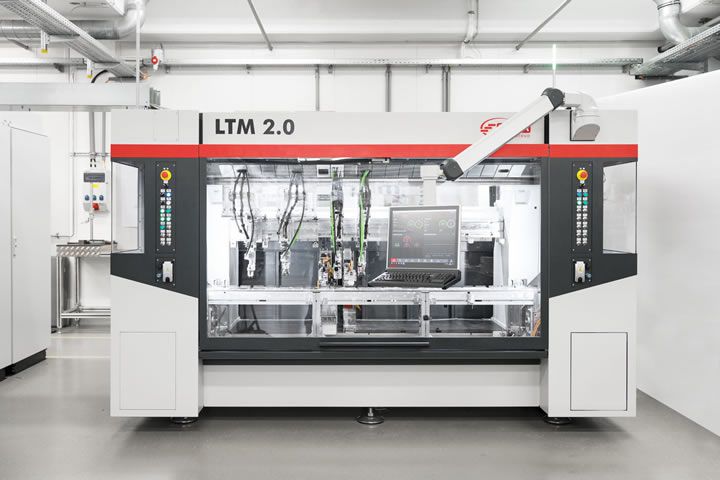
A "compact automation" is a mechatronic system that performs a whole series of consecutive production steps autonomously. "Compact" refers to the small dimensions, in the millimeter and centimeter range, of the products to be processed.
The rise of modular robots and the importance of drive train design
As part of an in-house robot build, optimizing the drive train that powers and controls each joint is vital to the robot's performance. The most effective way of achieving this is by developing the drive train as a complete module.
The most compact Motion Control System on the market
FAULHABER is introducing a new Motion Control System. More precisely: The world's smallest Integrated Motion Controller.
Optimizing Material Handling Processes for Increased Efficiency
Over the past few years, all aspects of the warehousing sector have been automated and this naturally includes the materials handling processes. This automation has increased efficiency across the board as well as improving employee safety and productivity.
DC microdrives bring dynamics into handling
Miniature drives and microdrives can be found in virtually all areas of automation technology and have a correspondingly wide variety of applications. These range from medical technology and laboratory automation.
Autonomous towing robots speeding up material handling
With omnidirectional movement and smart docking with virtually any warehouse cart in under 20 seconds, these new robots are making material handling faster and safer.
Motors and Motion Control Technologies in Orthopedic Surgical Robotics
Motors found inside orthopedic tools normally serve as the primary power source for driving devices like bone saws, drills or shavers. In these variable speed applications, motors need to be exceptionally small in diameter, lightweight & capable of running at high speed.
When to Choose a 4pole DC Motor
A 4pole design is stronger than a 2pole equivalent but can also fit within the same space and weight envelope. Greg Dutfield of maxon UK explains.
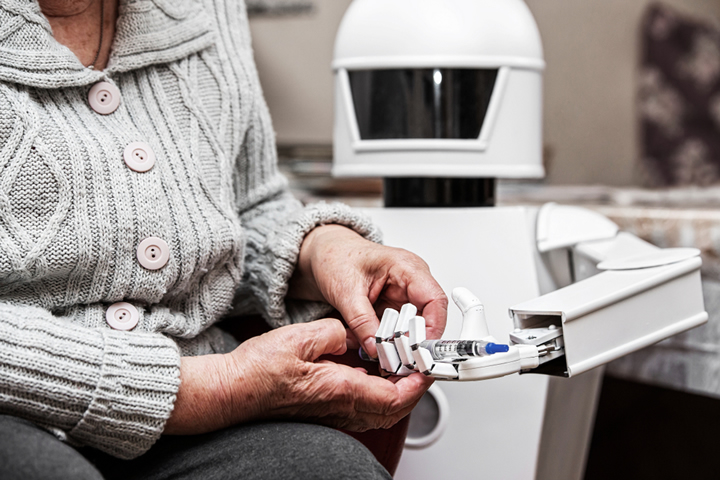
Can robots care? - Coreless motors driving patient care robots
FAULHABER's SR motor series is ideal for healthcare robot applications. Supplied by EMS in the UK and Ireland, the motors are designed for optimum power and performance while minimising weight and size.
How to Select the Right Motor for Your Robot
As both an industry and an entire class of technology, robotics changes and advances rapidly. Whether as a hobbyist or seasoned robotics engineer, you need to know each component inside and out. You should also know how to choose between several different variations.
Design and Operation Features of a BDC Motor Controller
The design and functionality of a DC motor controller depend on the characteristics of
the motor and the electronic system it powers. Using the example of a brushed DC
motor controller, we'll consider its operating principles and circuit design.
Records 1 to 15 of 34
Featured Product

High Performance Servo Drives for localized and distributed control applications from Servo2Go.com
Engineered to drive brushless and brush servomotors in torque, velocity or position mode, Servo2Go.com offers a broad selection of servo drives in a wide range of input voltages and output power levels.