We recently hosted a webinar titled: “Unlock Value-Stream Productivity with Robotic Cutting”. During this webinar, we polled audience members. Our first question: Have you looked at automating fabrication tasks in the past. Most respondents said yes, they had, in fact, explored this.
 Have You Looked at Automating Fabrication Tasks in the Past? Why Didn’t You?
Have You Looked at Automating Fabrication Tasks in the Past? Why Didn’t You?

Article from | Robotmaster
We recently hosted a webinar titled: “Unlock Value-Stream Productivity with Robotic Cutting”. This webinar provided an overview of the latest cutting market trends and looked at some of the challenges fabricators face. Audience members were also able to see game-changing robotic cutting technology and better understand how that technology is enabling fabricators to overcome challenges and unlock value-stream productivity.
During this webinar, we polled audience members. Our first question: Have you looked at automating fabrication tasks in the past. Most respondents said yes, they had, in fact, explored this.
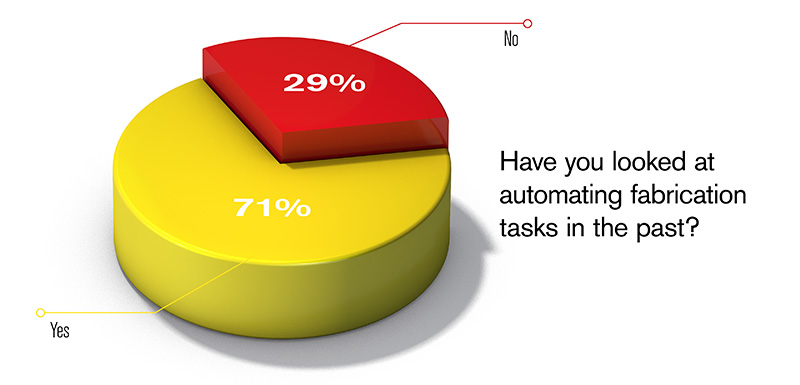
To be honest, we weren’t surprised. As fabricators are under intense pressure to increase production outputs while still struggling with a challenging skilled labor market, it is not surprising that they are looking at automation as a solution.
However, those who considered automating ultimately did not. We asked audience members to identify why they did not automate their fabrication tasks.
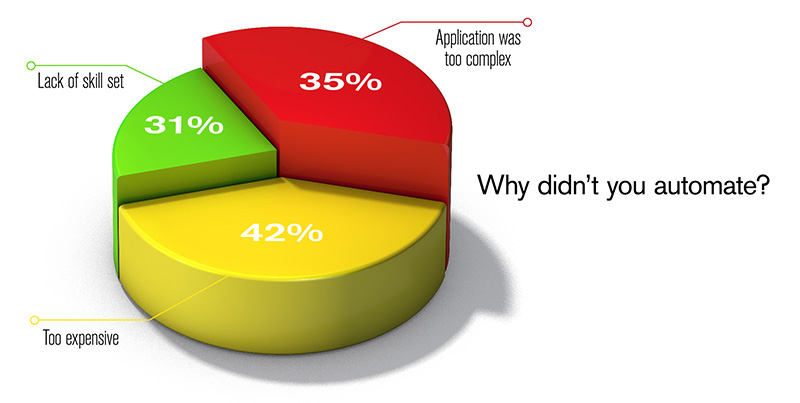
As the pie chart shows, there were three reasons attendees did not automate: (1) it was too expensive, (2) the application was too complex, and (3) they couldn’t find someone with the right skill set to help them.
The most popular answer was tied to the cost associated with automation. Automating can require a substantial investment. There is the physical cost of the equipment, the cost of implementing the automated solution in the facility, and the cost of programming. Furthermore, there can be additional costs such as the addition of a robot operator and training.
The second most popular answer was that their application was too complex. Automation has come a long way; however very customized solutions can drive the price up significantly so it really depends on the long-term usage of a system to determine whether the investment will yield a positive ROI. Our team often encounters situations in which the fabricator believes their parts are simply too complex to automate.
Finally, the lack of skill set. We all know the pressure fabricators have been under to try to acquire skilled labor of any kind let alone someone who knows how to implement an automated solution. Faced with what seems a daunting, if not impossible, task, business owners are understandably cautious about introducing automation.
Our poll included one last question. This time, we asked attendees to identify areas in which they successfully automated. We wanted to understand how they were currently programming their robots.
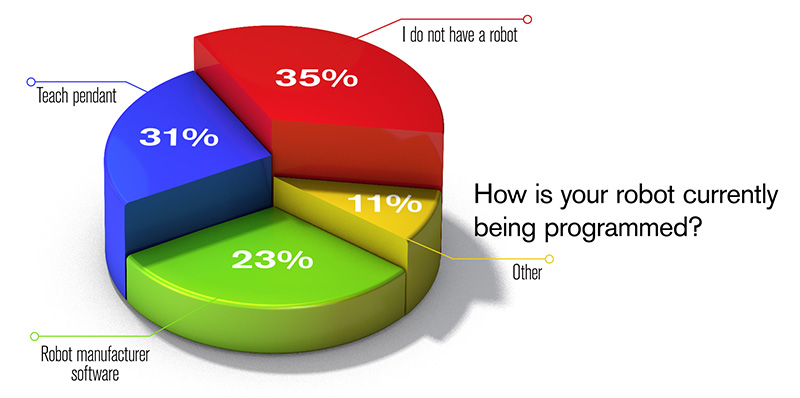
Roughly a third of attendees did not have experience programming robots of any kind. However, the remainder—65 percent—did. Nearly a third said they used the teach pendant method, which again didn’t surprise us. Overtime, we have seen a decrease in teach pendant usage as manufacturers have seen a decrease in mass production. Today, one-offs or smaller production runs are becoming more common. With this switch, pressures to program faster, keep robots in production, and increase output have led to a wider adoption of robot programming software.
With our questions out of the way, it was time to discuss solutions. We began by tackling the cost problem. To better understand the overall cost of automating, we recommended working with an experienced robotic integrator. An integrator will work to familiarize themselves with the process that needs to be automated, the target output, and desired results. They will then make a recommendation and provide an estimated return on investment (ROI) so the fabricator can better understand how long it will take for the automated solution to pay for itself.
The second major obstacle identified by our attendees had to do with the perceived complexity of the process they wished to automate. Often the hurdle in these situations is the programming method. Using a teach pendant to get into hard-to-reach areas or programming a part that has a lot of complexity can be extremely time consuming and tedious. A robotic integrator will take this into consideration and suggest a programming method that will yield the most optimal results. Generally, simple parts can be programmed using the teach pendant with a very good programming-time to production-time ration. However, programming for complex parts is more efficient when using programming software like Robotmaster. This software can take the part profiles from a CAD model and then generate robot trajectories from it. Programming complex parts is drastically easier and will result in better outcomes when done via a programming software.
The skilled labor challenge is admittedly a tougher obstacle to overcome, however, the right software can lend a helping hand. When considering automation, you should look at programming tools that require little to no programming or robotic expertise. Solutions like Robotmaster contain embedded process knowledge and easy to use programming tools that enable anyone to quickly program with confidence. The best part? Once a program is created, users can simulate the program to ensure it is error and collision free. More importantly, they can confirm the program will deliver the desired results.
Ultimately, if you were interested in automation, worked with an experienced integrator to explore this option, and did not end up with a viable automation solution in the past, we suggest you continue to explore it. Technology is evolving so quickly that it is possible that your fabricating tasks can now be automated!
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow

Robotmaster
Robotmaster, a Hypertherm Associates brand, is an offline, is an offline robot programming software that helps manufacturers maximize their robot's productivity with easy and efficient robot programming for a variety of applications such as cutting, trimming, milling, welding, spraying, polishing, sanding, grinding, deburring, and more. Robotmaster uses integrated CAD/CAM functionality to make robotic programming easy and intuitive for everyone, even first-time users.
Other Articles
Trane® Saves Over 80 Hours of Robot Programming Time
3 Benefits of Working With a Robotic Integrator
How Simulation Enhances the Offline Programming Experience
More about Robotmaster
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

