Drivers and Restraints to the Collaborative Robot Market
Industries across sectors are now analyzing COVID pandemic effects on sales and growth. While American manufacturers took a hit early on, the sector experienced a 30-month high in December as some U.S. companies calmed supply chain chaos by turning to domestic sourcing options. Even so, short-term shutdowns required for COVID sanitation protocols and higher-than-expected worker absenteeism limited growth.
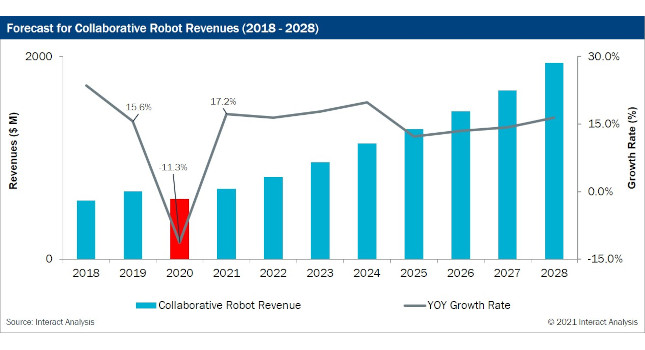
As a workaround to these issues, forward-thinking companies moved to integrate collaborative robotics. Cobots can offset the effects of worker absenteeism while offering an opportunity to increase social distancing, thus improving infection control. Yet the sector still experienced an 11.3% revenue drop as compared to the previous year.
A recent report by the smart manufacturing marketing firm Interact Analysis shows trends are improving. Research indicates the cobotics sector will see nearly 20% growth in 2021, and will continue growing at an annual rate of 15 to 20% through 2028. By that time, 15% of robotics industry sales will be collaborative robots.
Source: Interact Analysis
Future Use of Cobots
Manufacturers are demanding robots able to work alongside the human workforce instead of separated from it. Collaborative robots break down the boundaries between man and machine, taking over monotonous or heavy tasks like assembly or material handling. Cobot safety protocols protect workers during interactions when proper training is followed.
Increased mobility options offered by autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) opens up new opportunities for cobot use. Using this technology for material handling within storage and warehouse operations for goods transport was inevitable. Options continue to expand as payload capacities increase to 25 kg as gravity compensation and torque-sensing improves.
Meanwhile, cobots on the factory floor promise a reduction in health and safety risks for workers by limiting heavy lifting and other dangerous tasks while maintaining productivity. As manufacturers turn to collaborative robots for repetitious jobs, human workers are safer and workplace injuries reduced. According to ISA.org, Injuries figured into $15 billion dollars of losses for the manufacturing industry in 2017 alone. Taking such cost reductions into account explains how cobots offer such a quick return on investment.
Market Drivers for the Cobot Industry
Increasing demand by small to medium enterprises (SMEs) are expected to drive a significant part of the collaborative robotics market. These companies are drawn to the quick return on investment of most cobot technology; many cobot applications return their costs within the first year. Meanwhile, ventures of all sizes are using automation to drive productivity. Automation reduces operational costs, improves overall efficiency, and helps companies remain competitive in changing markets.
Growing automation demands within new industries is also a growth factor. While the automotive industry has traditionally accounted for a large portion of the cobot market, now other industries are discovering their usefulness. Heavy adoption within industries like pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, metal fabrication, and packaging is expected.
Additionally, cobot technology offers ease-of-use not found in traditional robotics. The industry is responding by offering more user-friendly models requiring less training. Some future cobots will be programmed by literally “going through the motions,” as an operator teaches the program by moving the cobot manually.
Restraints to Cobotics Growth
Industry 4.0 connects production processes to the outside world, including collaborative robots. Connected processes are vulnerable to rising cybersecurity risks. Cobots themselves can become vulnerable due to missing software updates. But poor network administration can also leave connected cobotics at risk to industrial espionage, malware installation, or automated attacks.
Secondly, cobot technology is changing faster than labor growth or standards can keep up with. New ANSI standards for Industrial Mobile Robot Safety Requirements work to standardize robot standards with mobile ones. Originally expected in late 2019, they have only recently been released.
Meanwhile, the need for workers with the right cobot skills has increased exponentially. Some have resorted to offering turnkey training through third party providers like Universal Robots to upskill and retain existing employees in more technical jobs. But a skills gap is expected to remain as demand for workers trained in human-machine collaboration increases. Some manufacturers may have to limit cobot expansion plans due to staffing constraints.
Finally, some manufacturers are turning to SCARA (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm) robots instead of cobots for certain applications. While these robots have small payload limitations and have limited flexibility, their high speed and accuracy make them a good choice for limited spaces or where fast, exact operations are required.
Technology writer Marla Keene works for AX Control, Inc, an industrial automation parts
supplier located in North Carolina. She writes about AR/VR, drones, green tech, artificial intelligence,and how technology is changing our world. Her articles have been featured in Wind Power Engineering, Food Industry Executive, and on other industry sites. Before working for AX Control, Marla spent twelve years running her own small business.
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

