Selecting the Right Alignment Method: From Passive Methods to fully Automated Fiber and Array Alignment Solutions
High-Throughput PIC Production Needs Precision Alignment Equipment for Photonics Arrays, Fibers, Lenses
Article from | PI USA
Photonics alignment is essential in manufacturing devices like silicon photonics (SiPh) components, fiber-optic systems, and advanced imaging equipment. Two primary alignment methods are employed: passive and active.
PI’s Fast Multi-Channel Alignment Algorithm (FMPA) enables ultra-fast, simultaneous alignment of multiple optical I/O channels across multiple degrees of freedom, achieving speeds orders of magnitude faster than traditional alignment systems.
Passive Alignment relies on mechanical fixtures or predetermined alignment features to position components without real-time feedback. This method depends on the inherent mechanical precision of these features to achieve alignment. While it can be cost-effective and suitable for applications with less stringent precision requirements, passive alignment often struggles to meet the nanoscale tolerances demanded by modern photonic devices. Achieving the necessary fabrication precision and reproducibility can be challenging, leading to increased costs and lower yields.
Active Alignment, in contrast, utilizes real-time feedback—such as optical power measurements—to adjust component positioning dynamically. This approach employs high-precision motion systems and intelligent algorithms to optimize coupling efficiency across multiple channels and degrees of freedom simultaneously. Active alignment is particularly advantageous for complex, high-performance photonic devices, offering superior precision and adaptability compared to passive methods.
Video: A double-sided waveguide alignment with the latest alignment algorithms can can be performed in less than one second.
The photonics industry's shift towards large-scale production, especially in SiPh devices, necessitates intelligent automation in testing and assembly processes. Alignment remains a time-intensive step, and advancements in active alignment technologies have significantly enhanced production economics. Modern systems equipped with advanced controls and built-in alignment algorithms can perform complex alignments rapidly, reducing tasks that once took minutes to mere seconds.
In summary, while passive alignment may suffice for certain applications, active alignment has become the preferred method for achieving the precision required in today's photonics industry. The integration of intelligent motion control systems and real-time feedback mechanisms has revolutionized alignment processes, enabling high-throughput production of sophisticated photonic devices.
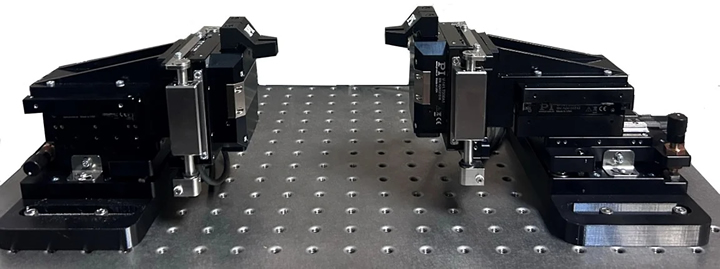
The F-141 Cost-Optimized, Compact Fast Alignment System for Photonics Arrays and Fiber Optics
Understanding Fiber Array Alignment
In optics and photonics, fiber array alignment refers to the precise positioning of optical fibers or collimators to efficiently couple light with photonic chips, waveguides, or other optical components. Photonic integrated circuits (PICs) rely on this alignment to facilitate critical functions such as data transmission, sensing, and computation.
To minimize optical losses and ensure maximum power transfer across all fiber array channels, advanced alignment hardware and intelligent algorithms are essential. This is particularly crucial in high-throughput production environments, where speed and accuracy directly impact performance and yield.
Video: High-Speed, Flexible Gantry Platform for Large-Area Photonic Testing & Assembly. This demonstration showcases a scan routine detecting the first light from an activated pixel on an LED marquee board, followed by a fine scan and gradient search for precise characterization.
Advanced Mechanisms and Algorithms for Smart Fiber Alignment and Optical Components Alignment
Early automated alignment systems relied on specialized mechanisms or stacks of expensive positioning stages. Nearly a decade ago, a breakthrough emerged with multi-axis piezo nanopositioning stages and hexapods, making them suitable for new applications in silicon photonics (SiPh) testing and assembly.
More recently, advancements in controller technology have enabled cost-effective stacks of industrial motion stages to achieve high-throughput, multichannel parallel alignment. This flexible architecture can even be applied to large substrates like printed circuit boards (PCBs). Additionally, compact air-bearing assemblies bring exceptional cleanliness to the process, addressing a growing concern in SiPh manufacturing. Compared to conventional microelectronics, back-end processes such as probing and assembly for SiPh devices demand significantly higher cleanliness standards to maintain high yields.
One of the most time-consuming challenges in industrial photonics alignment has been "finding first light"—the initial optical coupling step in wafer probing and device packaging. This process becomes even more complex when aligning both input and output channels, requiring precise dual-sided positioning to achieve even minimal coupling. However, recent innovations are transforming this process, significantly improving speed and efficiency.
Video: The PIlightning Photonics Algorithm revolutionizes first-light detection, delivering orders of magnitude faster signal acquisition and dramatically improving alignment efficiency.
Learn more on the latest high-throughput photonics alignment algorithms and alignment engines
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow

PI USA (Physik Instrumente)
PI is a privately held company that designs and manufactures world-class precision motion and automation systems including air bearings, hexapods and piezo drives at locations in North America, Europe, and Asia. The company was founded 5 decades ago and today employs more than 1700 people worldwide. PI's customers are leaders in high-tech industries and research institutes in fields such as photonics, life-sciences, semiconductors and aerospace.
Other Articles
Fast Hexapod Improves Aircraft Manufacturing Process
Fiber Alignment and Photonic Chip Test & Assembly Just Got Easier
Nanopositioning and Motion Control Solutions for the Semiconductor Industry
More about PI USA (Physik Instrumente)
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product


.jpg)