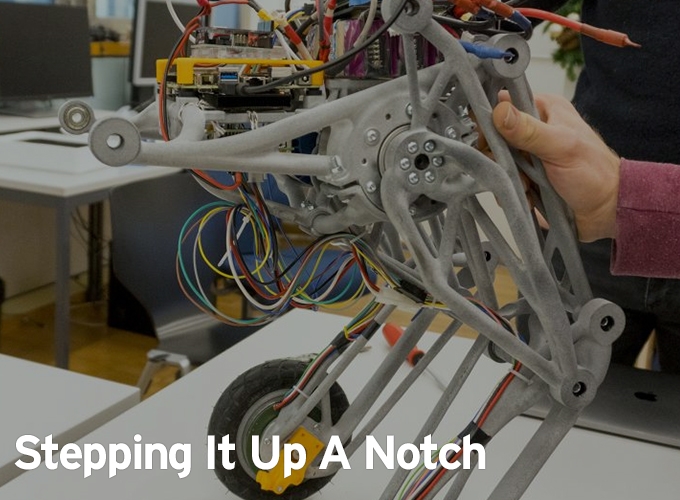
Stairs are still unsurmountable obstacles for many robots. Yet a young team at ETH Zurich is building a vehicle designed to negotiate steps with ease – by hopping.
Adrian Venetz | maxon motor
Reprinted with permission from the maxon motor drive.tech:
Stairs are still unsurmountable obstacles for many robots. Yet a young team at ETH Zurich is building a vehicle designed to negotiate steps with ease – by hopping.
"Ascento" is the name given to the sophisticated device by its creators, a team of eight students majoring in mechanical engineering and one in electrical engineering. The robot is quite special: It moves and balances on two wheels. From an engineering standpoint, this is significantly more difficult than building a device on four wheels. However, a bipedal robot provides much better mobility and adaptability to different terrain types.
That's not all: The main goal of the nine up-and-coming engineers is to make the robot leap. They want it to be able to jump high, like a kangaroo, and land again safely on its two wheels. “This would enable the robot to master stairs and other obstacles,” student Florian Weber explains. The Ascento team originated from a focus project. In this type of project, undergraduate students of various disciplines have a chance to apply their knowledge to a concrete project – from the initial idea to a functioning prototype.
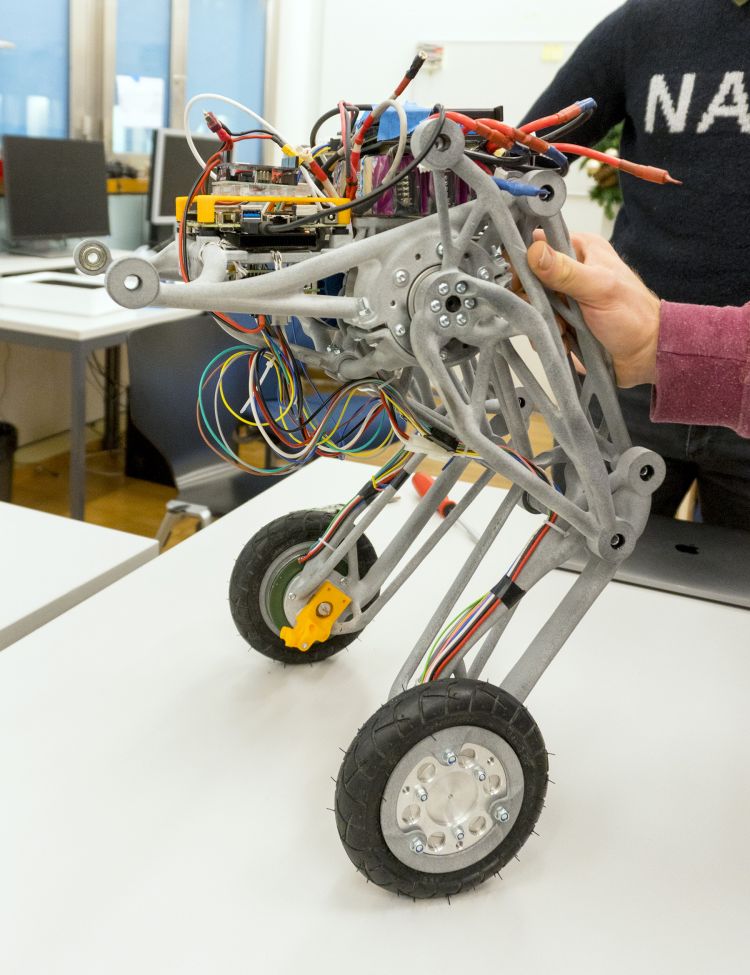
The special feature of the Ascento is that it is designed as an inverted pendulum: The center of gravity is above the axis. As a result, the Ascento is able to stand and move only as long as it is powered and actively maintaining balance on its wheels – similar to a standing human, who continuously has to expend energy to maintain balance. This makes the Ascento comparable to a Segway, which is also driven by two wheels that are on the same axis and requires a controlled drive to maintain balance.


The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow

maxon group
maxon is a leading supplier of high-precision DC brush and brushless servo motors and drives. These motors range in size from 4 - 90 mm and are available up to 500 watts. We combine electric motors, gears and DC motor controls into high-precision, intelligent drive systems that can be custom-made to fit the specific needs of customer applications.
Other Articles
Automate 2025 Q&A with maxon group
Understanding Torque and Speed in Electric Motors
How Parvalux Is Helping to Develop the Next Generation of Conveyor Systems
More about maxon group
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product